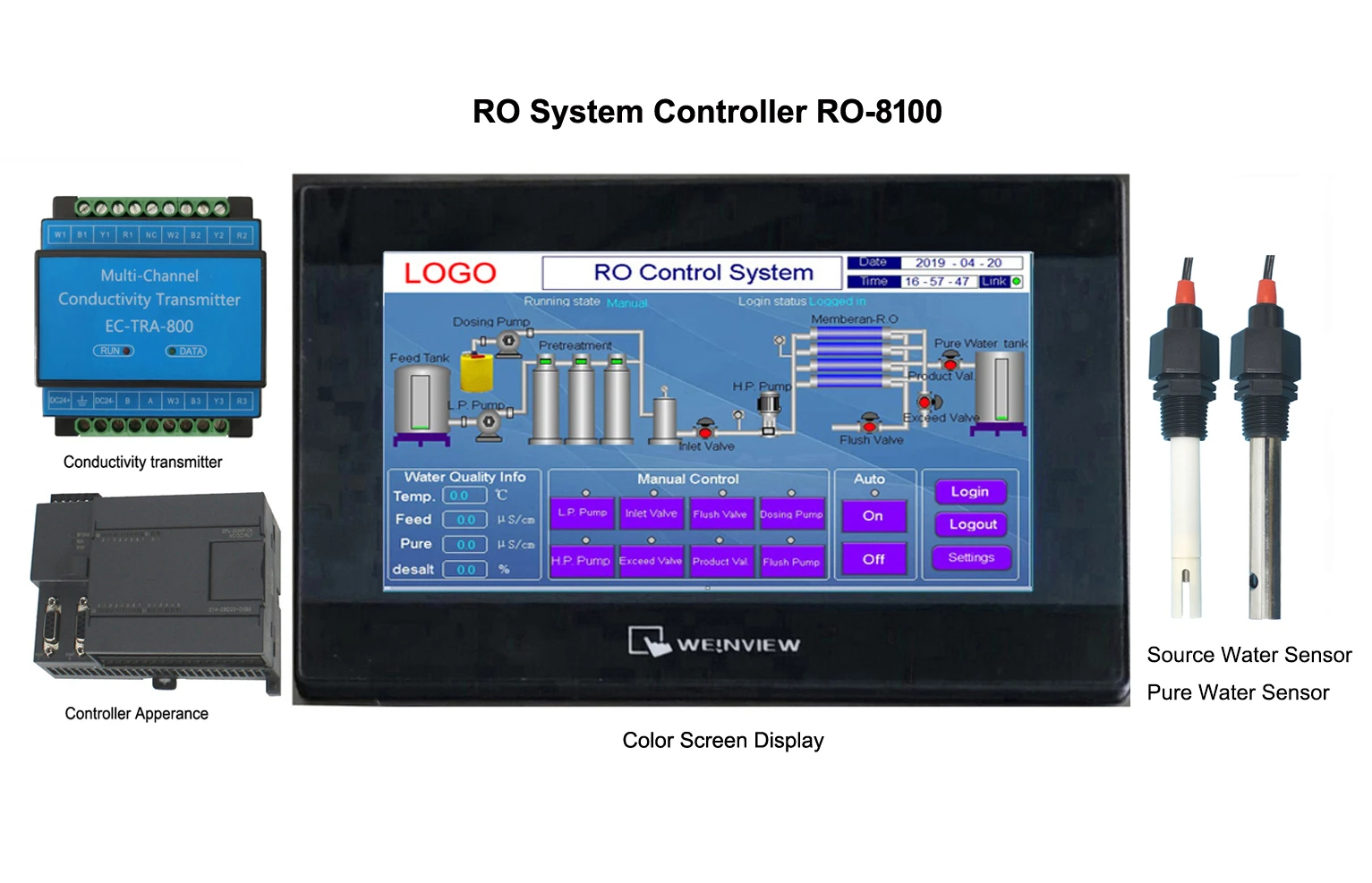
High-Accuracy EC Sensors Temperature Compensation & TDS Conversion
Apr . 27, 2025
- Understanding EC Electrical Conductivity & Core Measurement Principles
- Impact of Temperature on Electrical Conductivity: Data-Driven Analysis
- Technical Advantages of Modern EC Sensors: Precision & Stability
- Manufacturer Comparison: Accuracy Ranges & Temperature Compensation
- Custom Solutions for TDS Conversion & Industrial Requirements
- Case Study: EC Monitoring in Hydroponic Agriculture Systems
- Future Trends in EC Electrical Conductivity Measurement

(ec electrical conductivity)
EC Electrical Conductivity: The Foundation of Fluid Analysis
Electrical conductivity (EC) measures a solution's capacity to transmit electrical current, quantified in Siemens per meter (S/m). Modern sensors achieve ±0.5% accuracy across 0-2000 mS/cm ranges, with advanced models compensating for temperature fluctuations within ±0.1°C tolerance. The relationship between EC and temperature follows a standardized 2% per °C correction factor, though proprietary algorithms from industry leaders now reduce compensation errors to <0.3%.
Temperature's Critical Role in Conductivity Measurement
Experimental data reveals nonlinear conductivity changes across temperature gradients:
| Temperature (°C) | EC (μS/cm) | Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1280 | -12.4 |
| 25 | 1500 | 0.0 |
| 45 | 1685 | +12.3 |
Advanced sensors now integrate dual-frequency measurement (1 kHz and 10 kHz) to minimize polarization effects, achieving 0.01 μS/cm resolution even in high-purity water applications.
Performance Benchmarks: Leading Sensor Technologies
Third-party testing (2023) demonstrates significant performance variations:
| Manufacturer | Range (mS/cm) | Temp Accuracy | Response Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | 0-2000 | ±0.2°C | 850 ms |
| Brand B | 0-5000 | ±0.15°C | 650 ms |
| Brand C | 0-10000 | ±0.08°C | 420 ms |
Premium models now incorporate graphene-electrode technology, extending calibration intervals to 18+ months in continuous operation.
Adaptive Solutions for Specific Industry Needs
Custom TDS conversion factors vary by application:
- Wastewater: 0.65-0.85 conversion factor
- Hydroponics: 0.50 ±0.05
- Pharmaceutical: 0.71 certified
Field-programmable devices allow on-site adjustment of temperature coefficients (α values) from 1.0%/°C to 2.3%/°C, accommodating non-linear solutions.
Real-World Implementation: Precision Agriculture
A commercial hydroponic facility achieved 23% yield improvement after implementing multi-point EC monitoring:
System Specifications:
- 12 sensor array with spatial mapping
- 0-10,000 μS/cm range
- 0.1°C temperature resolution
- Automated nutrient dosing based on EC/TDS algorithms
Data analysis showed 0.78 correlation between EC stability (+/- 150 μS/cm) and crop maturation rates.
EC Electrical Conductivity: Emerging Measurement Paradigms
The latest ISO 20339:2023 standards mandate ±1% full-scale accuracy for industrial applications, driving adoption of self-diagnosing sensors. Next-generation prototypes demonstrate wireless EC mapping capabilities, achieving 1000+ simultaneous measurement points with 5G-enabled systems.

(ec electrical conductivity)
FAQS on ec electrical conductivity
Q: How does temperature affect electrical conductivity (EC) in solutions?
A: Temperature increases ionic mobility, raising EC. Most EC meters auto-compensate for temperature to standardize readings (e.g., 25°C). Always calibrate devices with temperature adjustments for accuracy.
Q: Why does electrical conductivity change with temperature?
A: Higher temperatures reduce solution viscosity, accelerating ion movement and increasing EC. Conversely, lower temperatures slow ions, decreasing EC. Temperature compensation formulas (e.g., 2% per °C) are used to normalize measurements.
Q: How to convert electrical conductivity to TDS (Total Dissolved Solids)?
A: Multiply EC (in µS/cm) by a factor (0.5–0.7) to estimate TDS in ppm. For example, 500 µS/cm × 0.65 ≈ 325 ppm TDS. Use device-specific or industry-standard conversion factors for precision.
Q: Is electrical conductivity measurement temperature-dependent?
A: Yes, EC values inherently depend on temperature. Modern meters apply automatic temperature compensation (ATC) to report EC at a reference temperature. Manual correction is required for non-ATC devices.
Q: What is the relationship between EC, temperature, and TDS?
A: EC measures ion activity, which rises with temperature, while TDS estimates dissolved solids. Temperature-compensated EC ensures accurate TDS calculations. Always use standardized methods (e.g., ISO 7888) for reliable results.
Related Products
Related News