Residual Chlorine Meter: A Key Guarantee for Ensuring Water Quality Safety
Mai . 22, 2025
Residual chlorine, as an important indicator in the process of water disinfection, directly affects the safety and hygiene of drinking water and various industrial water. Low residual chlorine content may lead to poor disinfection effect and the growth of pathogenic microorganisms; Excessive residual chlorine content can affect taste and even pose a potential threat to human health. Therefore, accurate measurement of residual chlorine levels in water samples is crucial. The Residual Chlorine Meter, as a precision instrument specifically designed for this purpose, plays an indispensable role in the field of water quality monitoring.
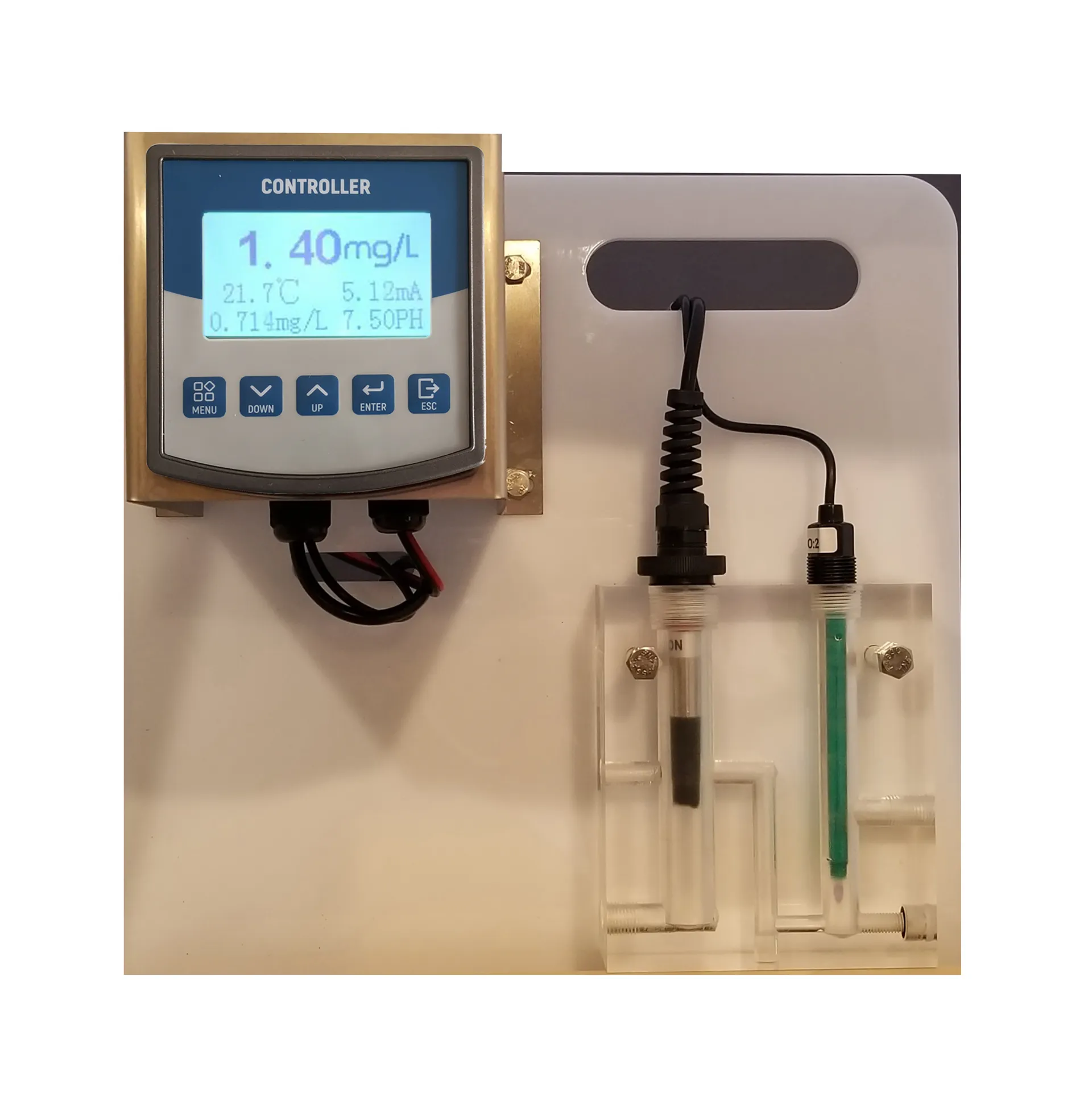

The precision of Residual Chlorine Meter is its core value
Different types of water samples, such as tap water, swimming pool water, industrial cooling water, etc., have different ranges of chlorine content and interfering substances. A high-quality free chlorine meter needs to be able to adapt to these differences, eliminate interference factors, and provide stable and reliable measurement results. This precision relies on sophisticated instrument design, high-quality sensors, and advanced signal processing technology. For example, the Residual Chlorine Meter using Ampere method can calculate the residual chlorine concentration by measuring the current change between the residual chlorine and a specific electrode, effectively avoiding interference from factors such as turbidity and chromaticity, and providing more accurate measurement data.
In addition to precision, the practicality and ease of use of the Residual Chlorine Meter are also crucial
Modern chlorine probe are typically equipped with clear and intuitive display screens, user-friendly interfaces, and convenient for users to perform rapid measurements and data recording. Many instruments also have automatic calibration functions, reducing manual errors and improving measurement efficiency. In addition, some advanced Residual Chlorine Meters can also be connected to data acquisition systems to achieve real-time data transmission and remote monitoring, providing a more convenient means for water quality management.
The application range of Residual Chlorine Meter is very wide
During the production process of tap water, residual chlorine sensors are used to monitor the residual chlorine content at various stages to ensure that the final drinking water meets national standards. In swimming pools, residual chlorine meters are used to maintain appropriate levels of residual chlorine, prevent bacterial growth, and ensure the health of swimmers. In industrial water treatment, Residual Chlorine Meter is used to control the amount of residual chlorine added, prevent equipment corrosion and biofilm formation, and improve production efficiency.
In short, the chlorine ppm sensor is an important tool for ensuring water quality safety. Its precision, practicality, and ease of use make it an indispensable device in the field of water quality monitoring. With the continuous advancement of technology, the performance of Residual Chlorine Meter is also constantly improving, providing us with more reliable and efficient water quality assurance, safeguarding people's health and quality of life.
Residual Chlorine Mete FAQs
What is the working principle of Residual Chlorine Mete?
Residual Chlorine Mete mainly uses the following two methods for measurement:
Colorimetric method (DPD method):
The residual chlorine in the water sample reacts with N, N-diethyl-phenylenediamine (DPD) reagent to form a red compound, and the residual chlorine concentration is calculated by measuring the absorbance with a spectrophotometer.
Applicable scenarios: laboratory or portable testing, high accuracy, suitable for low concentration residual chlorine (0.015 mg/L).
Electrochemical method (membrane electrode method):
Using current or potential sensors, residual chlorine undergoes redox reactions on the electrode surface, resulting in changes in current or potential that are proportional to the concentration of residual chlorine.
Applicable scenarios: Online monitoring (such as water treatment plants, swimming pool circulation systems), fast response, suitable for long-term continuous measurement.
Why do drinking water and swimming pools have to use Residual Chlorine Mete to monitor residual chlorine? What are the safety standards?
The main function of residual chlorine is sterilization and disinfection, but too high or too low can affect safety:
Drinking water (WHO/EPA standard):
Free residual chlorine is 0.22 mg/L (≥ 0.2 mg/L at the end of the pipeline to ensure continuous disinfection).
Exceeding the standard may produce carcinogenic byproducts such as trihalomethanes (THMs).
Swimming Pool Water (International Standard):
Free residual chlorine 13 mg/L (indoor swimming pool) or 25 mg/L (outdoor swimming pool).
Chemical chlorine (chloramine) should be less than 0.5 mg/L, otherwise it may irritate the eyes and skin.
How to calibrate Residual Chlorine Mete? How to determine the calibration frequency?
Calibration method:
Standard solution calibration: Use a known concentration of residual chlorine standard solution (such as 1 mg/L or 5 mg/L) for calibration.
Zero point calibration: Adjust the instrument zero point with chlorine free water (such as distilled water).
Calibration frequency:
Laboratory instruments: calibrated before each use.
Online monitoring device: calibrated weekly or monthly (depending on the usage environment and stability).
Attention: The shelf life of DPD reagents is relatively short (usually 6 months), and expiration can affect accuracy.
What factors will affect the measurement results of Residual Chlorine Mete? How to reduce errors?
Common interference factors and solutions:
PH value: The DPD method is most accurate at pH 6.26.5, and if it is too high or too low, the buffer solution needs to be adjusted.
Oxidant interference: Ozone, bromine, and chlorine dioxide can also react with DPD, and specific reagents or calibration algorithms need to be selected.
Turbidity/Chromaticity: Turbidity water samples require filtration or compensation mode (supported by some advanced instruments).
Temperature: Electrochemical sensors require temperature compensation (usually automatically calibrated).
How to optimize water treatment process with online Residual Chlorine Mete?
Waterworks: Real time adjustment of chlorine dosage to avoid insufficient disinfection or excessive chlorine residue.
Swimming pool circulation system: linked with automatic chlorine adding machine to maintain stable residual chlorine and reduce manual detection.
Industrial cooling water: Monitor residual chlorine to prevent microbial growth (such as Legionella), while avoiding equipment corrosion.
Data recording and alarm: When exceeding the standard, trigger an alarm and record historical data for compliance review.
Related Products
Related News