Understanding Turbidity Meter Types: Which One Is Right for Your Application?
Apr . 21, 2025
Monitoring turbidity—an indicator of water clarity—is vital for applications ranging from drinking water treatment to environmental monitoring. Choosing the right device begins with understanding the different turbidity meter types available on the market. Each type uses varying detection methods, sensitivity ranges, and measurement units to assess the presence of suspended particles in liquids.
The most common turbidity meter types include nephelometers and ratio turbidimeters. Nephelometers measure scattered light at a 90-degree angle from the light source, which is ideal for low to moderate turbidity levels. Ratio turbidimeters measure light at multiple angles (forward scatter, side scatter, and backscatter), making them suitable for higher turbidity or more complex sample matrices.
In addition, there are laboratory turbidity meter types and portable field models. Laboratory meters often offer high precision and compliance with standards like ISO 7027 or USEPA Method 180.1. Portable meters are battery-operated, rugged, and designed for quick testing in remote or harsh conditions. Online or in-line turbidity meters are automated systems used for continuous turbidity monitoring in real-time—especially critical for municipal water treatment and industrial process control.
Choosing among the turbidity meter types depends on your specific application, desired sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and budget. Whether you're evaluating environmental runoff or ensuring safe drinking water, selecting the right turbidity meter ensures data accuracy and regulatory compliance.

How a Turbidity Test Apparatus Works in Quality Control
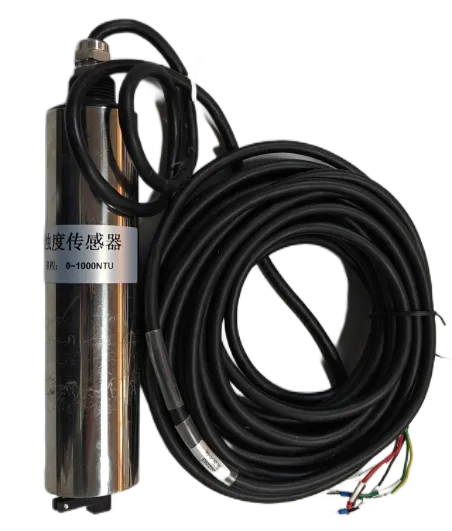
The turbidity test apparatus is a cornerstone of water quality testing in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, beverage production, and wastewater treatment. This equipment measures the cloudiness or haziness of a liquid, which is typically caused by particles too small to be seen with the naked eye but large enough to scatter light.
A complete turbidity test apparatus typically consists of a light source, a detector, and a sample cuvette. The light source passes through the sample, and the detector reads the amount of light that is either absorbed or scattered. The intensity of this scattered light correlates with the turbidity of the sample, expressed in Nephelometric Turbidity Units (NTU) or Formazin Nephelometric Units (FNU), depending on the measurement method.
Modern turbidity testing setups often include microprocessor-controlled interfaces, digital data logging, and calibration features. For more advanced uses, dual-beam and infrared-based turbidity test apparatus offer higher accuracy and are less sensitive to color or temperature fluctuations in the sample.
In quality control labs, consistency is key. Repeated, reliable measurements using a properly calibrated turbidity test apparatus ensure product safety and meet strict compliance standards. For example, pharmaceutical companies must monitor turbidity to ensure the clarity of injectable solutions, while breweries rely on it to control the haze in beverages.

What Affects Turbidimeter Price and How to Get the Best Value
When it comes to purchasing lab equipment, the turbidimeter price is a significant factor. But like any precision instrument, price should be weighed alongside performance, durability, and long-term cost of ownership. Several variables affect the turbidimeter price, including brand reputation, measurement range, accuracy, certifications, and available features.
Entry-level portable turbidimeters may start at $200–$500 and are suitable for field testing and basic applications. Mid-range benchtop models typically range from $1,000 to $3,000 and include enhanced accuracy, digital displays, multi-point calibration, and data transfer capabilities. At the high end, advanced in-line turbidimeters or process analyzers designed for industrial and municipal use can exceed $10,000.
Another cost factor is regulatory compliance. Devices certified for use in EPA or ISO-regulated environments usually cost more due to rigorous testing and calibration requirements. Similarly, turbidimeter price increases when extra functions are added—such as self-cleaning sensors, real-time alarms, or integration with SCADA systems.
To get the best value, customers should consider not only the initial turbidimeter price but also the maintenance costs, calibration frequency, sensor replacement, and ease of use. Choosing a reliable manufacturer with a strong support network can save thousands over the lifespan of the equipment.
How to Use a Turbidimeter: A Practical Guide With Turbidimeter PPT Resources
Understanding the theory behind turbidity is essential—but knowing how to operate a turbidity meter effectively is just as critical. Many institutions and training programs use visual aids like turbidimeter ppt presentations to teach water quality professionals how to use these devices correctly.
A turbidimeter ppt usually covers key aspects such as the types of turbidimeters, measurement principles (e.g., nephelometry vs. attenuation), standard operating procedures, calibration techniques, and common troubleshooting tips. It’s also a useful tool for understanding how to interpret results, maintain equipment, and comply with industry standards like EPA 180.1 or ISO 7027.
Practically, using a turbidimeter involves filling a clean cuvette with a water sample, inserting it into the device, and reading the result on the display. Calibration should be performed using standards like formazin, which provides a known turbidity value to compare against. Some modern turbidimeters allow automatic calibration with pre-filled calibration kits.
Hands-on training paired with a turbidimeter ppt presentation helps technicians understand potential pitfalls, such as air bubbles in the sample, scratched cuvettes, or ambient light interference. Mastering these techniques ensures accurate, repeatable results—whether in a lab setting or out in the field.
Comparing Turbidity Meter Types for Industrial, Laboratory, and Environmental Use
Different industries have different needs when it comes to measuring turbidity, and comparing turbidity meter types helps buyers select the most suitable device. For laboratories, precision is paramount. These environments favor benchtop meters that offer high-resolution readings and support for multiple calibration points. They are perfect for testing drinking water, pharmaceutical samples, and food products.
In environmental monitoring, portability and ruggedness are critical. Field-use turbidity meter types include handheld meters with waterproof casings, GPS tracking, and long battery life. These are ideal for researchers collecting turbidity data in rivers, lakes, and estuaries. Some also include Bluetooth or USB data export functions for seamless reporting.
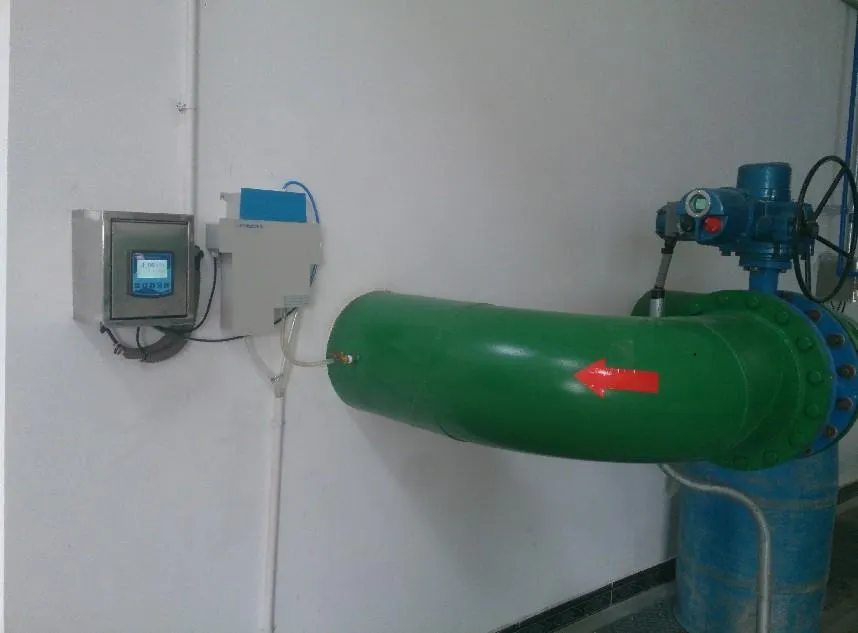
Industrial and municipal facilities typically favor online or in-line turbidimeters. These systems continuously monitor water flow, often as part of a larger automation or SCADA system. Built with robust materials, they are equipped to handle high temperatures, chemical exposure, and constant operation. These turbidity meter types often include cleaning mechanisms to prevent fouling and ensure consistent results over long periods.
Each turbidity meter type serves a unique role, and choosing the right one depends on the specific operational needs, regulatory requirements, and budget. Whether you're measuring the clarity of spring water or controlling effluent discharge, there's a turbidity meter designed to meet your expectations.
Turbidity Controller FAQs
What is turbidity, and why is it important to measure?
Turbidity refers to the cloudiness or haziness of water caused by suspended particles. These particles scatter and absorb light, reducing water clarity. Measuring turbidity is important because it indicates water quality and potential contamination. High turbidity can interfere with disinfection processes and may indicate the presence of harmful microorganisms. Monitoring turbidity is vital for drinking water safety, environmental studies, and industrial processes.
How do different turbidity meter types compare?
Turbidity meter types vary in design and use-case. Nephelometers are best for low turbidity samples, while ratio meters handle high-turbidity water or complex suspensions. Benchtop meters offer high precision for lab use, portable meters are ideal for field testing, and online meters provide continuous monitoring. The right choice depends on your testing environment, desired accuracy, and compliance standards.
What should I look for in a turbidity test apparatus?
A reliable turbidity test apparatus should offer accuracy, ease of calibration, and durable construction. Look for features like a high-quality light source, sensitive detector, and user-friendly interface. Calibration options, compliance with regulatory standards, and robust customer support are also essential. Some advanced apparatuses also offer cloud connectivity and data storage for audit-ready reports.
Why does turbidimeter price vary so much between models?
The turbidimeter price is influenced by many factors including measurement range, accuracy, brand reputation, included features, and compliance certifications. Basic portable models are affordable but may lack data logging or advanced optics. High-end systems for industrial use offer greater durability, automation, and connectivity—justifying their higher cost. Always compare total cost of ownership, not just the upfront price.
Where can I find a good turbidimeter ppt for training or reference?
A turbidimeter ppt can be found from various sources including manufacturer websites, water quality associations, academic institutions, and online course providers. These presentations are valuable tools for learning about turbidity theory, instrument use, and regulatory standards. You can also request customized training materials from turbidimeter manufacturers or distributors, many of whom provide technical support and training sessions for their products.
Related Products
Related News