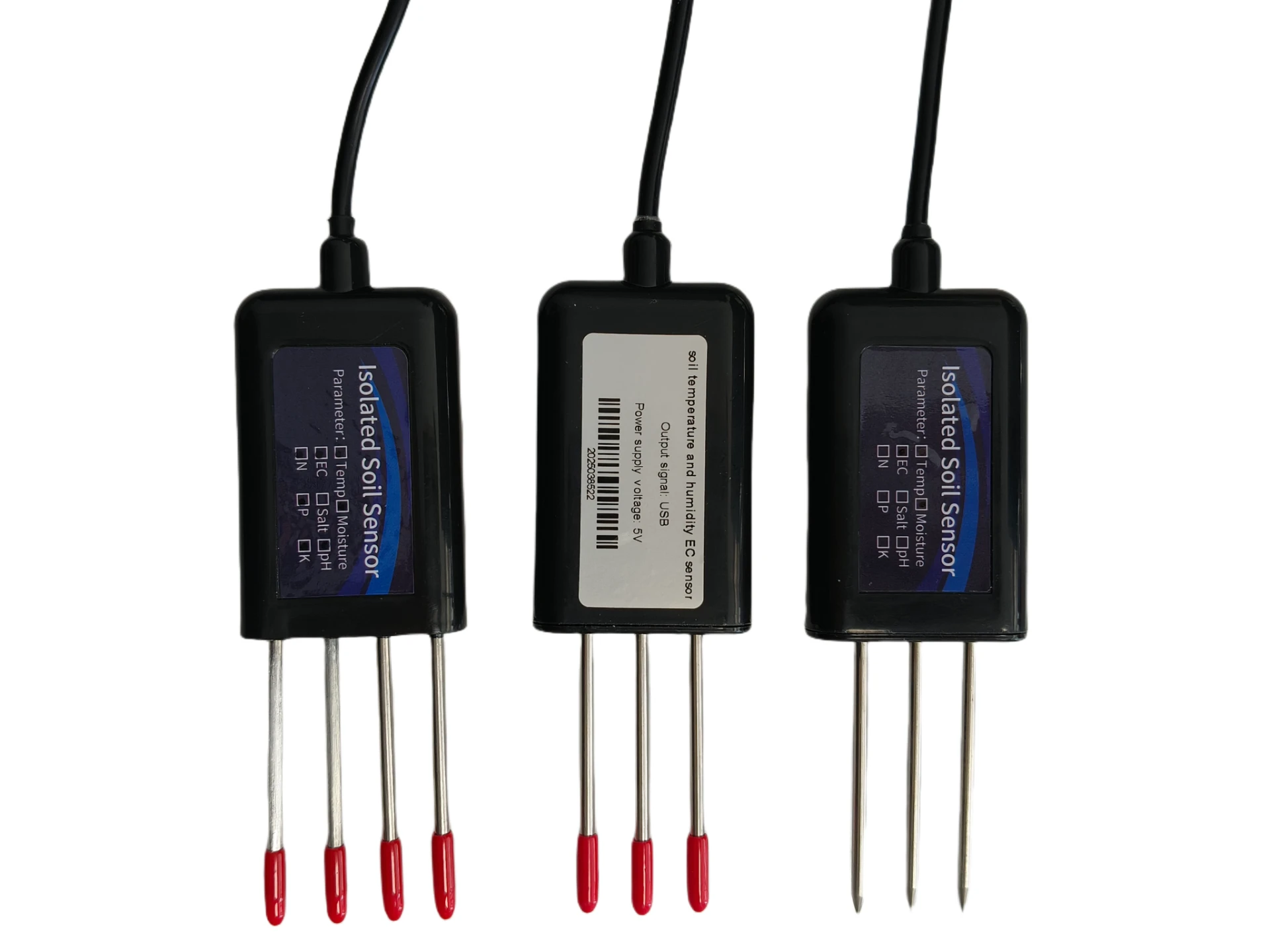
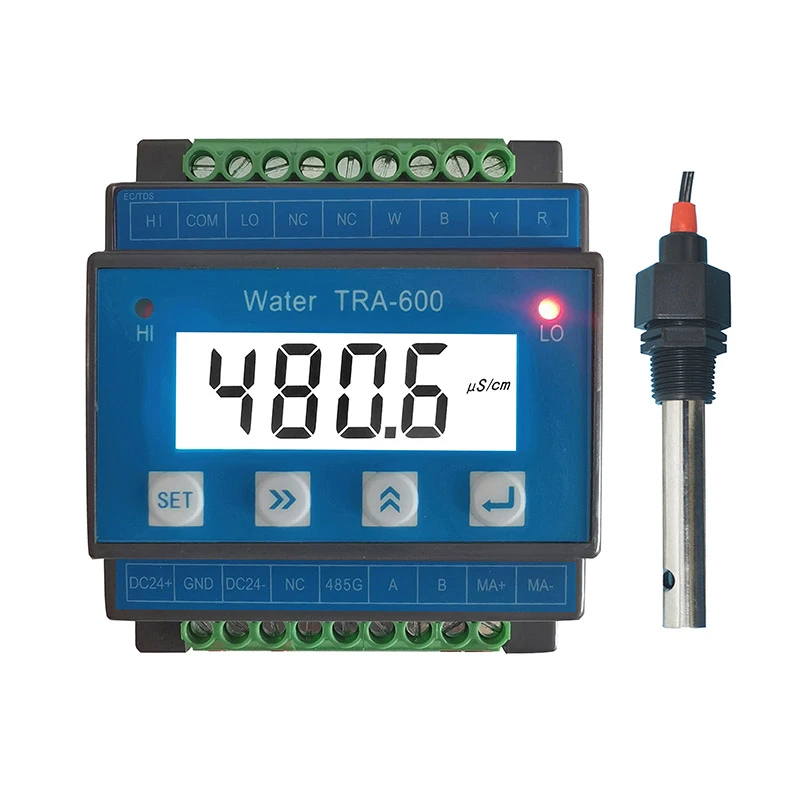
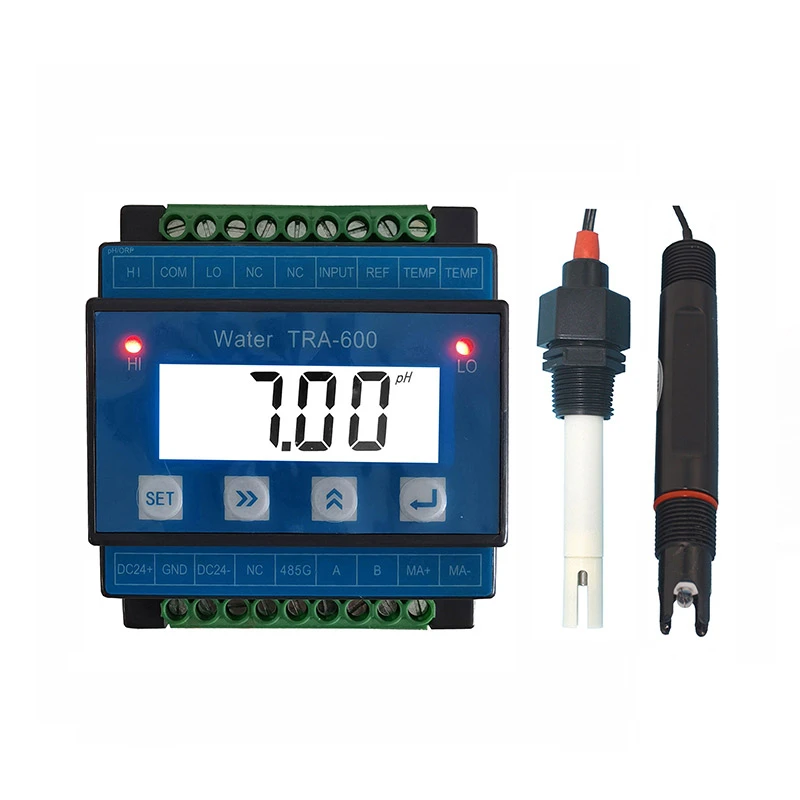
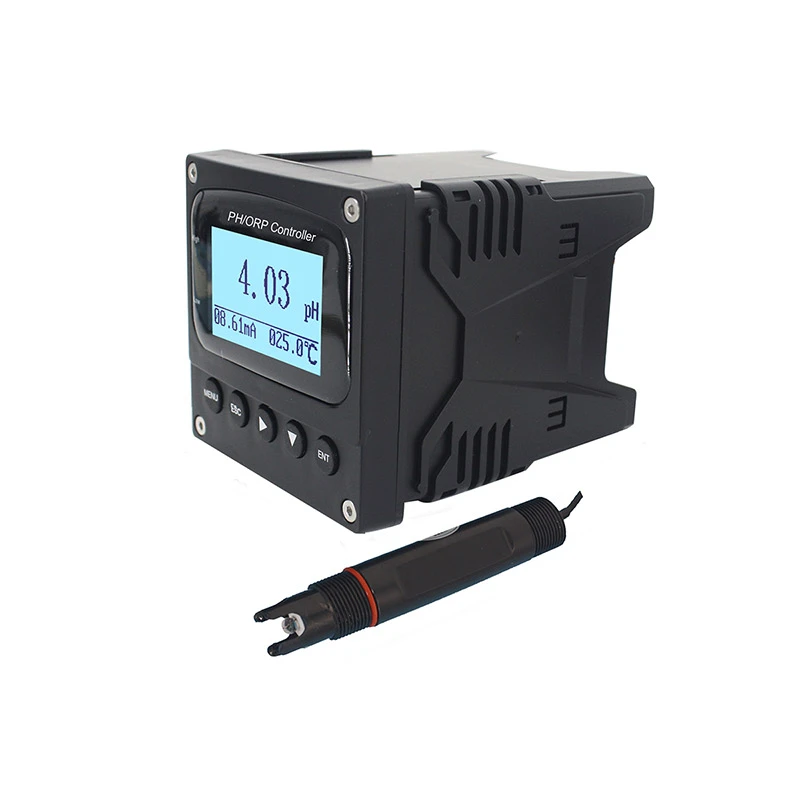
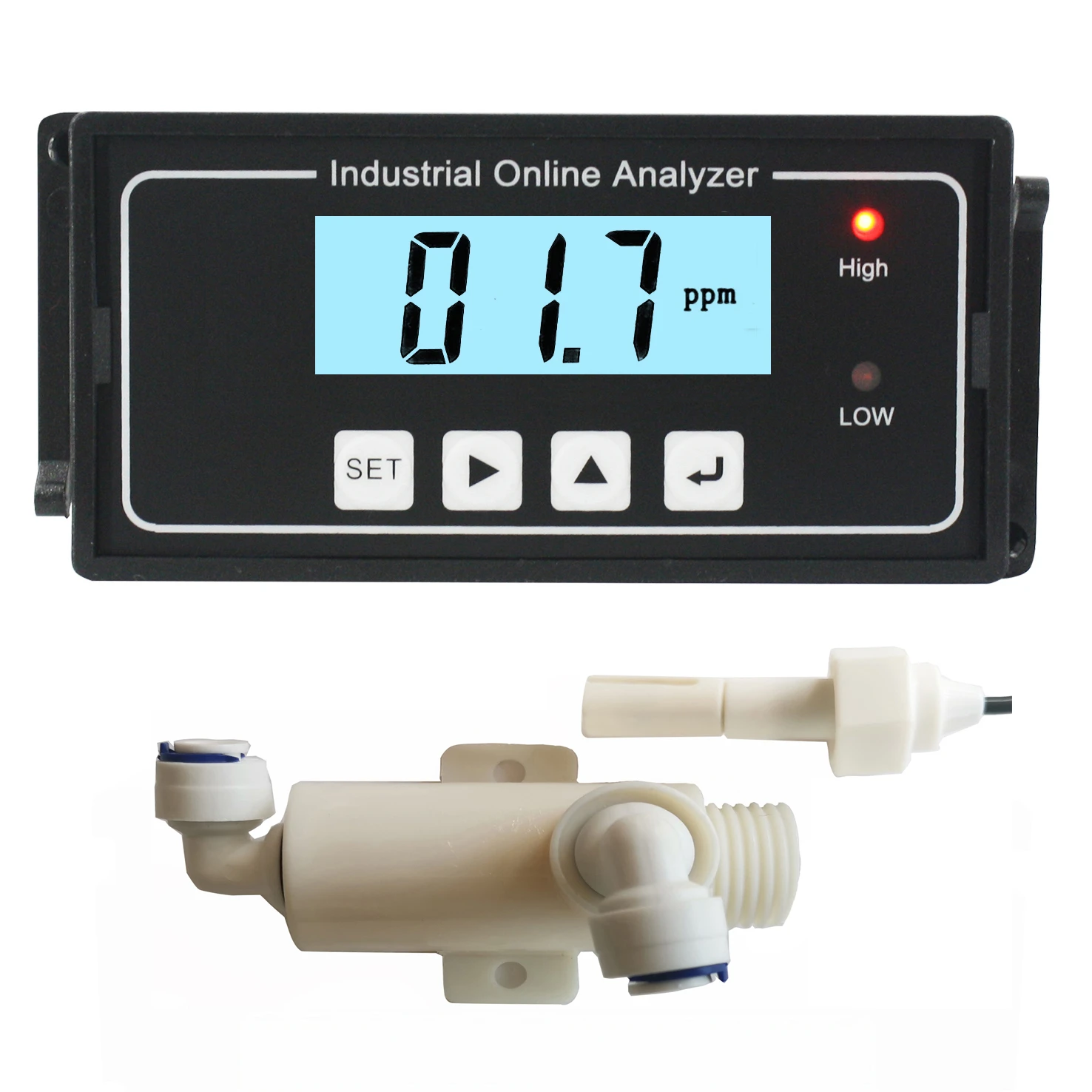
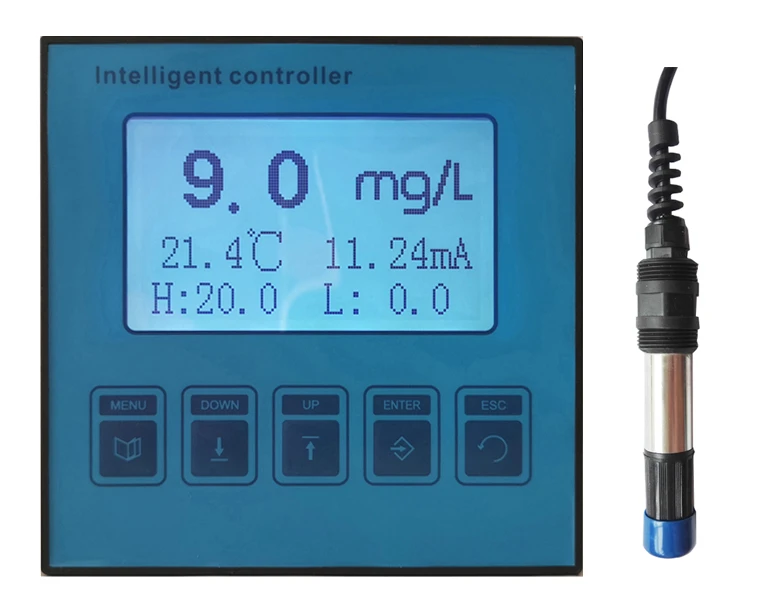
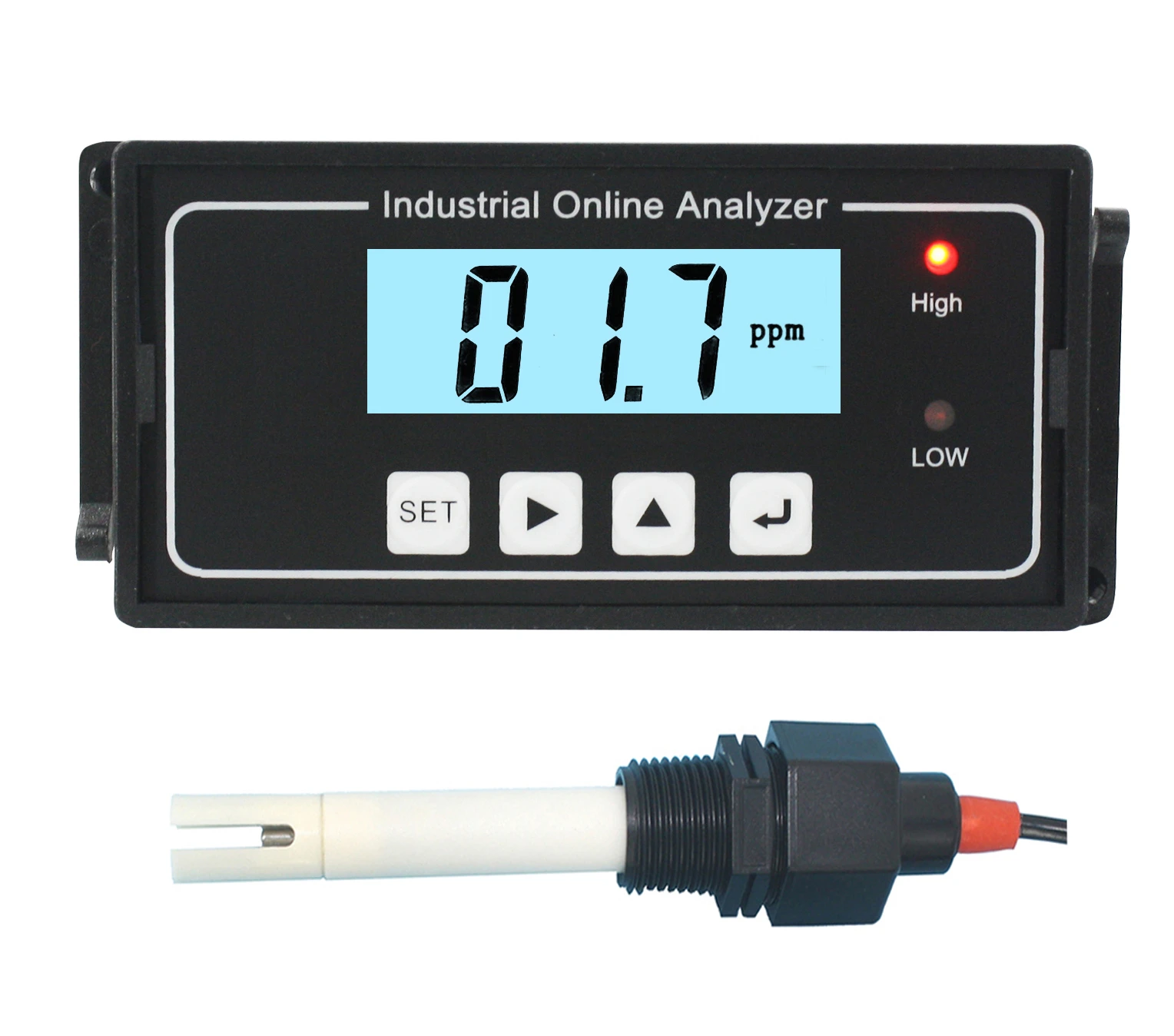
Accurate Salt Solution Conductivity Meters Lab & Industrial Use
Apr . 27, 2025
- Understanding the Basics of Conductivity in Aqueous Solutions
- Key Factors Influencing Salt Solution Conductivity
- Advanced Techniques for Accurate Conductivity Measurement
- Technological Innovations in Conductivity Monitoring Systems
- Comparative Analysis of Leading Conductivity Measurement Devices
- Custom Solutions for Industry-Specific Conductivity Requirements
- Real-World Applications and Success Stories

(conductivity of salt solution)
Understanding the Basics of Conductivity in Aqueous Solutions
The conductivity of salt solution
s is a critical parameter in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to environmental monitoring. Conductivity measures a solution’s ability to transmit electrical current, which depends on ion concentration and mobility. For instance, a 1M NaCl solution exhibits approximately 85 mS/cm at 25°C, while a 0.1M solution drops to around 12 mS/cm. This linear relationship between concentration and conductivity forms the foundation for applications like quality control and process optimization.
Key Factors Influencing Salt Solution Conductivity
Temperature, ion type, and solution purity significantly impact conductivity. Sodium ions (Na⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻) contribute differently to conductivity compared to divalent ions like Ca²⁺ or SO₄²⁻. Temperature compensation algorithms, such as linear 2%/°C corrections, are essential for accurate readings. Impurities as low as 0.5 ppm can alter conductivity by up to 3%, emphasizing the need for precise calibration protocols.
Advanced Techniques for Accurate Conductivity Measurement
Modern sensors employ four-electrode cells and digital signal processing to achieve ±0.5% accuracy across 0–200 mS/cm ranges. Automated temperature compensation (ATC) and self-cleaning electrodes reduce drift, ensuring stability in continuous monitoring. For example, systems with ATC maintain
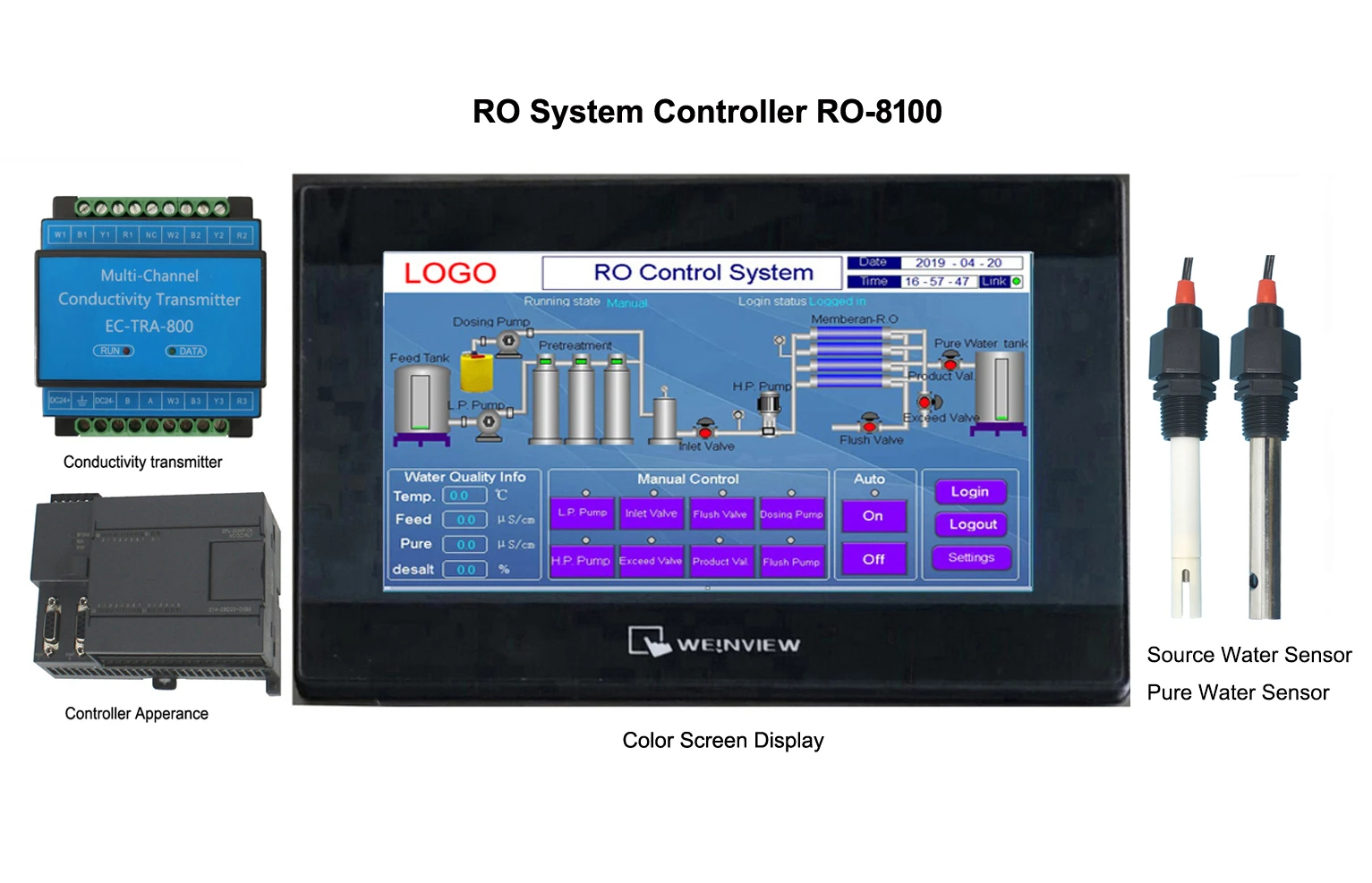
Technological Innovations in Conductivity Monitoring Systems
Leading manufacturers now integrate IoT capabilities, enabling real-time data logging and remote calibration. Multi-parameter probes combining conductivity, pH, and dissolved oxygen sensors reduce operational costs by 30% compared to standalone units. Wireless connectivity options like LoRaWAN extend deployment flexibility in harsh environments.
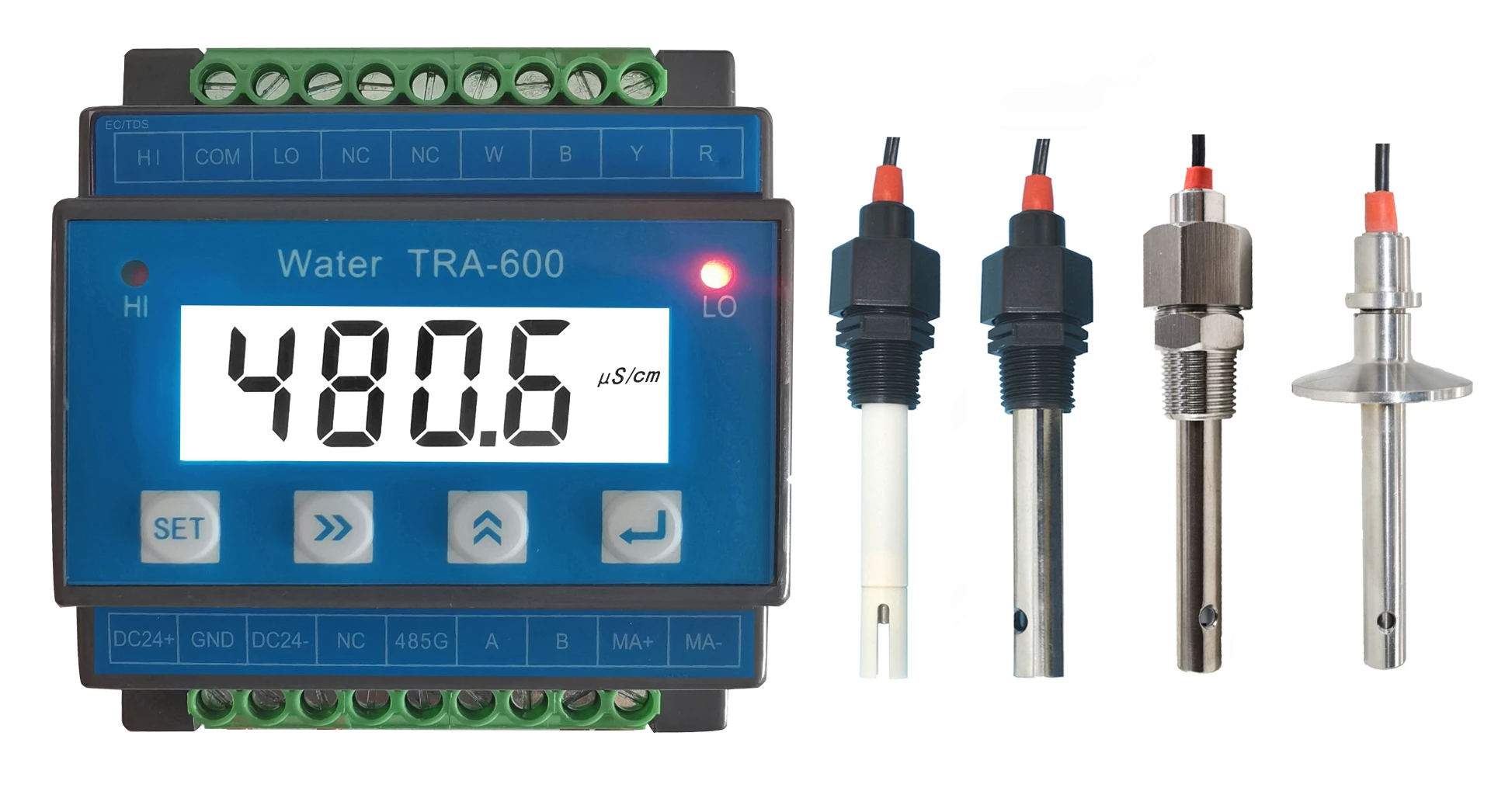
Comparative Analysis of Leading Conductivity Measurement Devices
| Brand | Range (mS/cm) | Accuracy | Temperature Range (°C) | IP Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | 0–200 | ±0.5% | -10 to 80 | IP68 |
| Brand B | 0–500 | ±1.0% | 0–50 | IP67 |
| Brand C | 0–1000 | ±0.2% | -20 to 120 | IP69K |
Custom Solutions for Industry-Specific Conductivity Requirements
Pharmaceutical manufacturers require USP -compliant systems with 0.01 µS/cm resolution for WFI (Water for Injection) monitoring. In contrast, wastewater plants prioritize 0–100 mS/cm ranges with anti-fouling coatings. Customizable alarm thresholds and MODBUS/Profibus outputs enable seamless integration with SCADA systems, reducing implementation time by 40%.
Real-World Applications and Conductivity of Salt Solution Optimization
A food processing plant achieved 15% energy savings by optimizing brine concentration using inline conductivity sensors. Another case saw a 90% reduction in calibration downtime through automated diagnostics in semiconductor ultrapure water systems. These successes demonstrate how precise aqueous solution conductivity management drives operational efficiency across sectors.

(conductivity of salt solution)
FAQS on conductivity of salt solution
Q: What factors affect the conductivity of a salt solution?
A: The conductivity of a salt solution depends on ion concentration, charge, and mobility. Higher salt concentration and ion charge increase conductivity, while temperature also enhances ion movement and conductivity.
Q: How is the conductivity of a solution measured?
A: Conductivity is measured using a conductivity meter or probe, which applies an electric field to the solution. The device calculates conductivity based on the solution’s ability to carry current, typically expressed in Siemens per meter (S/m).
Q: Why do aqueous salt solutions conduct electricity?
A: Aqueous salt solutions conduct electricity because salts dissociate into free ions (e.g., Na⁺ and Cl⁻) in water. These ions act as charge carriers, enabling the flow of electric current through the solution.
Q: How does temperature influence aqueous solution conductivity?
A: Rising temperature increases aqueous solution conductivity by reducing viscosity and accelerating ion mobility. However, extremely high temperatures may cause evaporation, altering concentration and conductivity.
Q: Can pure water conduct electricity like a salt solution?
A: Pure water has negligible conductivity due to minimal ion dissociation. Salt solutions, however, contain abundant ions from dissolved salts, making them far more conductive than pure water.
Related Products
Related News