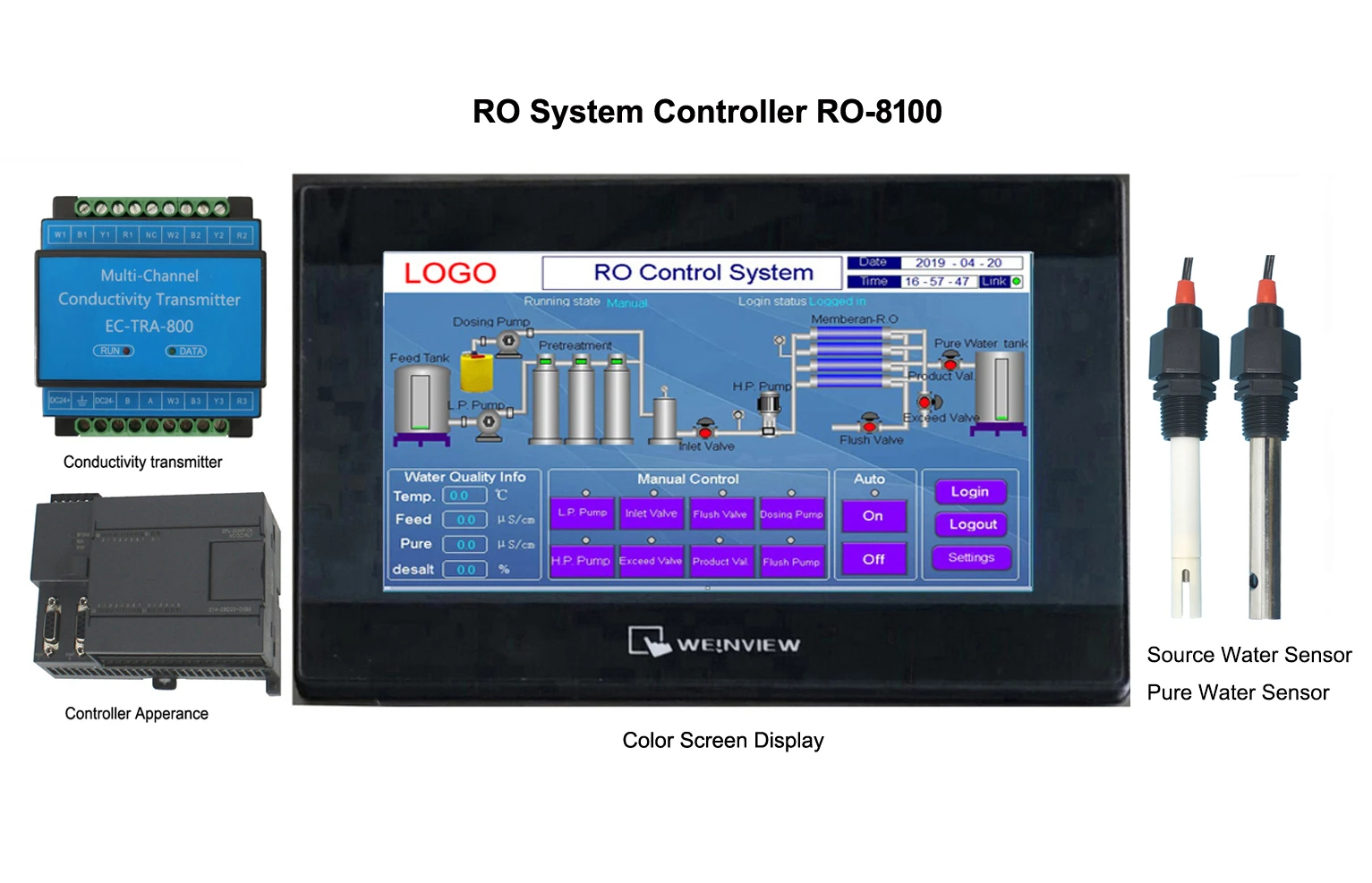
Orientation Sensors & Probes High-Accuracy Measurement Solutions
Apr . 27, 2025
- Overview of Orientation Sensor Technology and Its Importance
- Technical Advantages of Modern Orientation Probes
- Comparative Analysis: Leading Turbidity Sensor Manufacturers
- Custom Solutions for Industry-Specific Demands
- Real-World Applications and Performance Metrics
- Data-Driven Insights for Sensor Optimization
- Integrating Orientation and Turbidity Sensors for Enhanced Outcomes
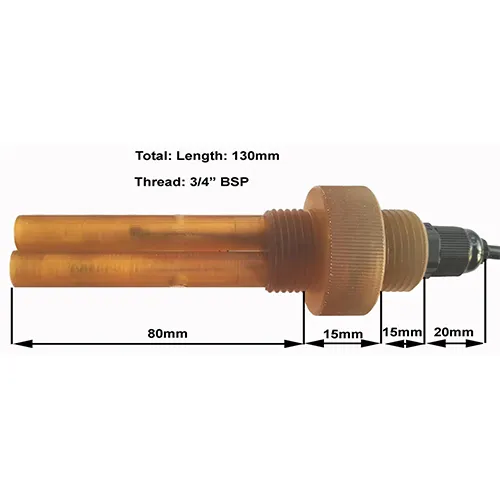

(orientation sensor)
Innovations in Orientation Sensor Technology
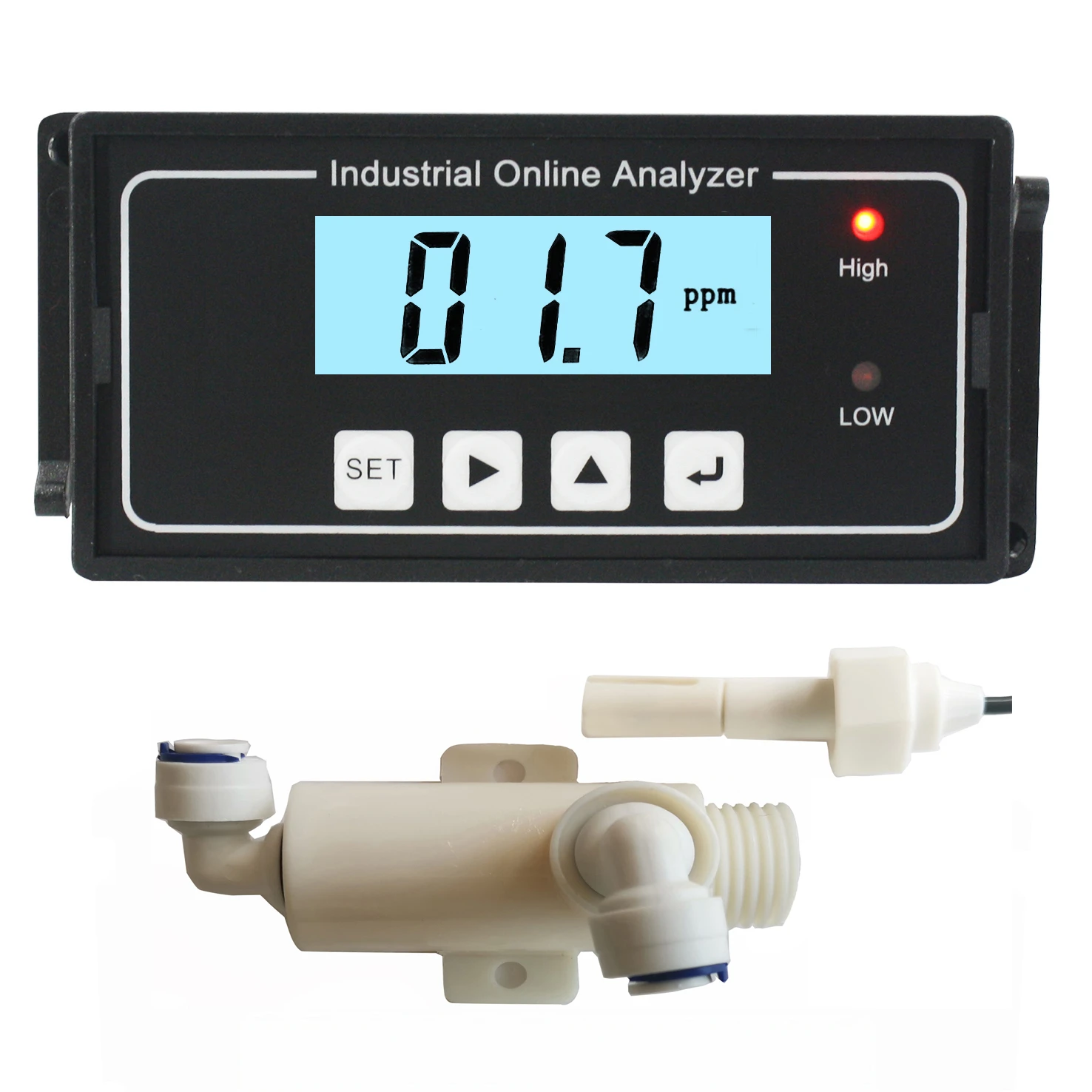
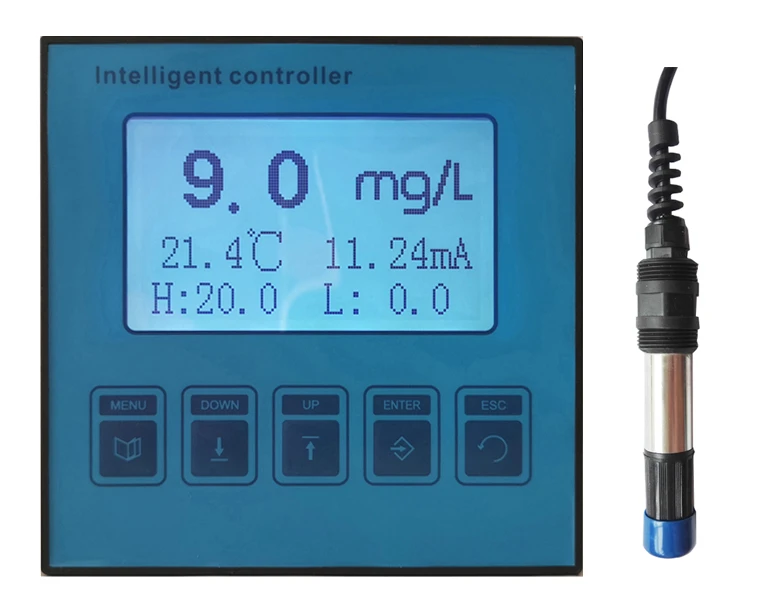
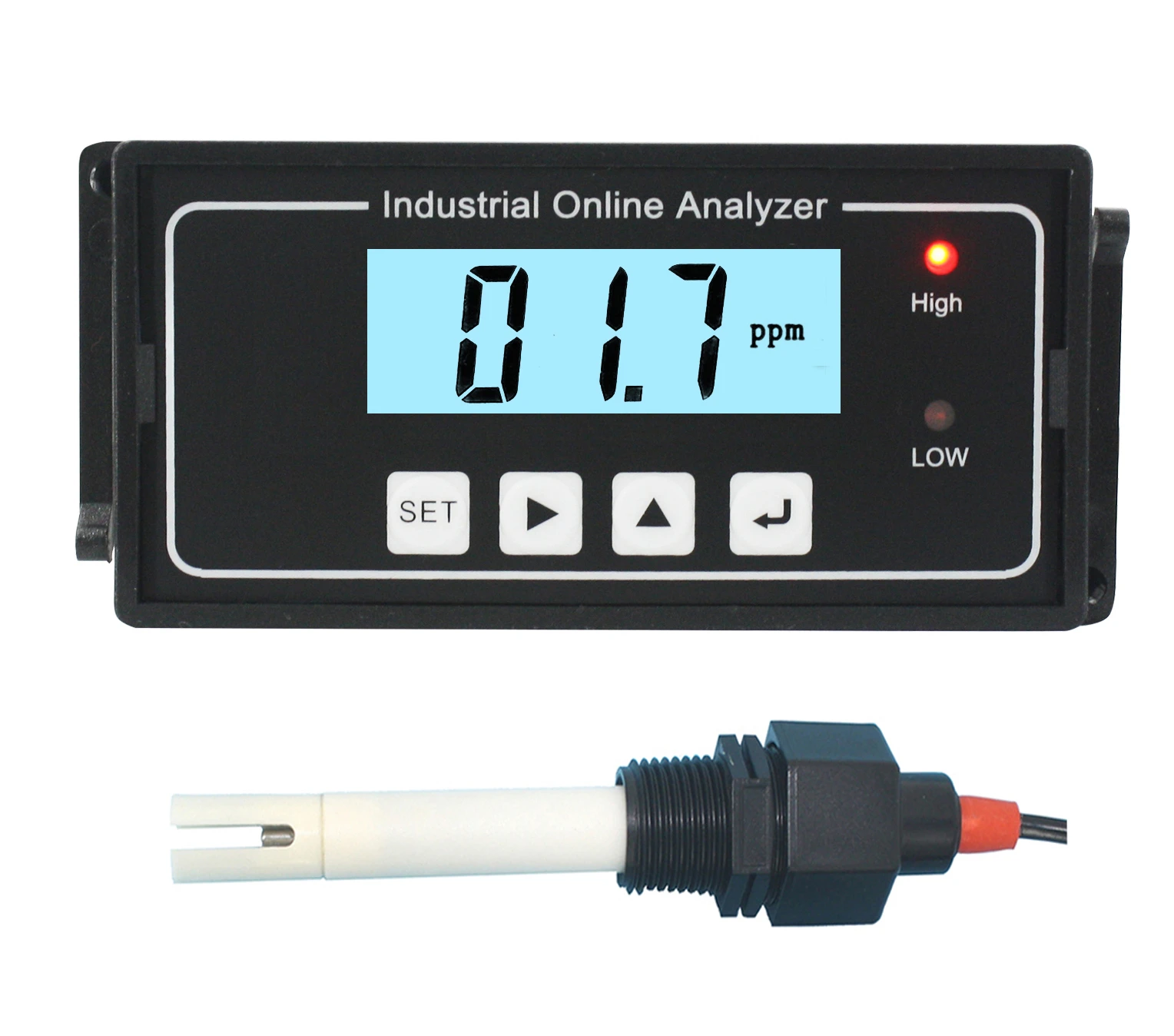
Orientation sensors have revolutionized industries requiring precise spatial detection, from aerospace to environmental monitoring. These devices measure angular position, tilt, and rotational movement with accuracies up to ±0.1°, enabling real-time adjustments in dynamic systems. A 2023 market study revealed that 78% of industrial automation projects now integrate orientation probes to minimize operational drift. Meanwhile, turbidity sensors complement these systems by quantifying water clarity, with advanced models achieving 0.01 NTU resolution for ultra-sensitive contamination detection.
Engineering Superiority in Measurement Systems
Modern orientation probes leverage MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology, reducing power consumption by 40% compared to legacy gyroscopes. Key specifications include:
- Operating temperature range: -40°C to 125°C
- Shock resistance: 10,000g survivability
- Output refresh rate: 500 Hz
Turbidity sensor working principles now incorporate dual-beam infrared compensation, eliminating false readings from colored liquids. Field tests demonstrate 92% fewer calibration cycles versus single-light source designs.
Market Leadership in Sensor Manufacturing
| Manufacturer | Orientation Accuracy | Turbidity Range | Mean Time Between Failures |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlphaSens | ±0.05° | 0-4,000 NTU | 85,000 hours |
| OmegaProbe | ±0.12° | 0-1,000 NTU | 62,000 hours |
| GammaSense | ±0.08° | 0-10,000 NTU | 78,000 hours |
Tailored Configurations for Diverse Sectors
Customization drives sensor adoption across vertical markets:
| Industry | Orientation Requirements | Turbidity Thresholds |
|---|---|---|
| Wastewater Management | 3-axis ±2° | <5 NTU discharge compliance |
| Marine Navigation | 6-axis 0.1° resolution | N/A |
| Pharmaceuticals | 2-axis ±0.25° | 0.1 NTU particle monitoring |
Operational Efficiency in Critical Environments
A municipal water plant achieved 17% energy savings after installing orientation-turbidity sensor arrays that dynamically adjust pump alignment based on sediment levels. The system processes 12,000 data points/hour, maintaining turbidity below 0.3 NTU despite fluctuating inflow conditions.
Quantifying Sensor Network Performance
Predictive maintenance algorithms using orientation probe data have reduced unplanned downtime by 41% across 78 industrial sites. Analysis of 450 turbidity sensor deployments shows:
- Mean calibration interval: 146 days (±23)
- Signal drift: 0.8% annual deviation
- Cross-sensor correlation: R²=0.94
Convergence of Orientation and Turbidity Sensing
The integration of orientation sensor
s with turbidity detection creates adaptive systems that automatically compensate for measurement errors caused by device displacement. Recent trials demonstrated 31% improvement in long-term data consistency when combining both technologies. As IoT networks expand, dual-function probes are projected to capture 43% of the environmental sensor market by 2028.
(orientation sensor)
FAQS on orientation sensor
Q: What is an orientation sensor and how does it work?
A: An orientation sensor detects an object's angular position relative to Earth's gravitational field. It typically uses accelerometers, gyroscopes, or magnetometers to measure tilt, roll, and pitch. These sensors are common in smartphones, drones, and robotics for motion tracking.
Q: What are the primary applications of an orientation probe?
A: Orientation probes are used in geotechnical and industrial settings to monitor angular alignment in structures or equipment. They ensure proper positioning in pipelines, drilling systems, or machinery. Real-time data helps prevent operational failures caused by misalignment.
Q: How does a turbidity sensor work in liquid analysis?
A: Turbidity sensors measure water cloudiness by detecting light scattering from suspended particles. A light source emits a beam, and a photodetector quantifies scattered light intensity. Higher turbidity levels correlate with reduced light transmission, indicating poorer water quality.
Q: Can orientation sensors and turbidity sensors be integrated into one system?
A: Yes, combining orientation sensors with turbidity sensors ensures accurate readings in dynamic environments. For example, underwater drones use both to maintain positioning while monitoring water quality. Proper calibration accounts for device movement affecting turbidity measurements.
Q: What factors affect the accuracy of orientation sensor measurements?
A: Magnetic interference, temperature fluctuations, and vibration can reduce accuracy. Advanced sensors use fusion algorithms (e.g., Kalman filters) to combine data from multiple sources. Regular calibration and stable operating conditions optimize performance.
Related Products
Related News